| GIS
|
|
|
The most widely used module is the Geographical Information System
(GIS). From here all georeferenced information can be queried from
the database or the response manaual by a mouse click.
After initiating the program, an overview map will be displayed to
the user.
The orientation for the user is easily accomplished by using the
coast kilometerage and zooming into the desired area, whereby the
kilometerage automatically transfers to a 500-m grid. The data
contents are also displayed in more detail when the displayed map
extent is enlarged. |
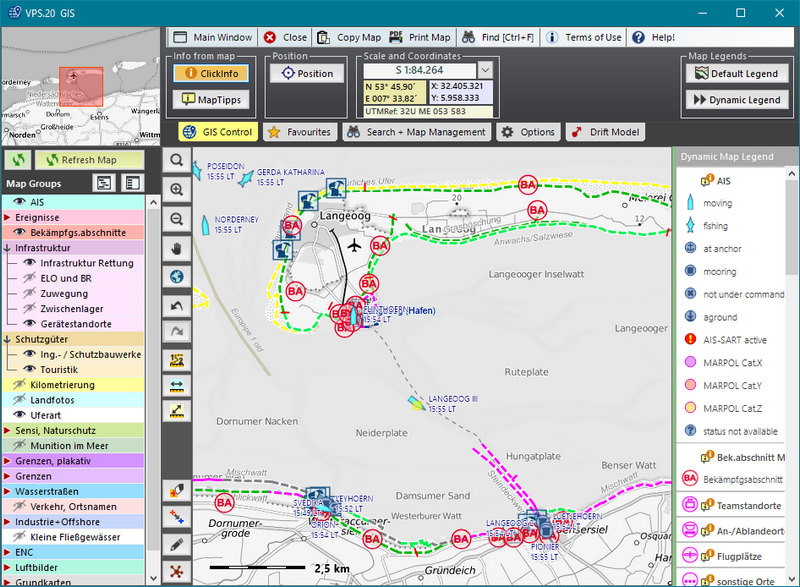 |
Through the activation of different layers, additional thematic data
can be displayed at the topographic master chart. For nearly every
symbol, additional information is available.
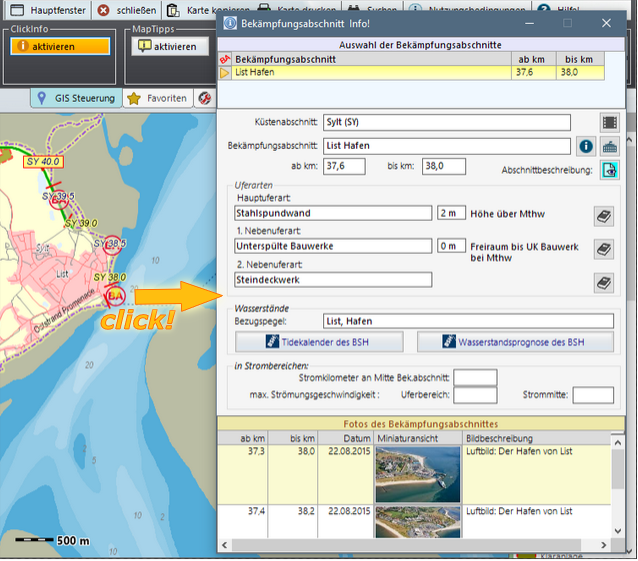
The GIS is linked to the datasets in the database and offers with `ClickInfo´
the answer to the question `What´s that?´, because the corresponding
database form opens with a click at the selected object.
Additionally, `MapTipps´are available for quick information. To
assign response-relevant information to individual coast sections,
the whole coast was segmented into response sections with a length
from 100 m up to max. 10 km. Ample data for every response
section-symbol are located within the database, and can be called up
with the `ClickInfo` function.
|
 |
|
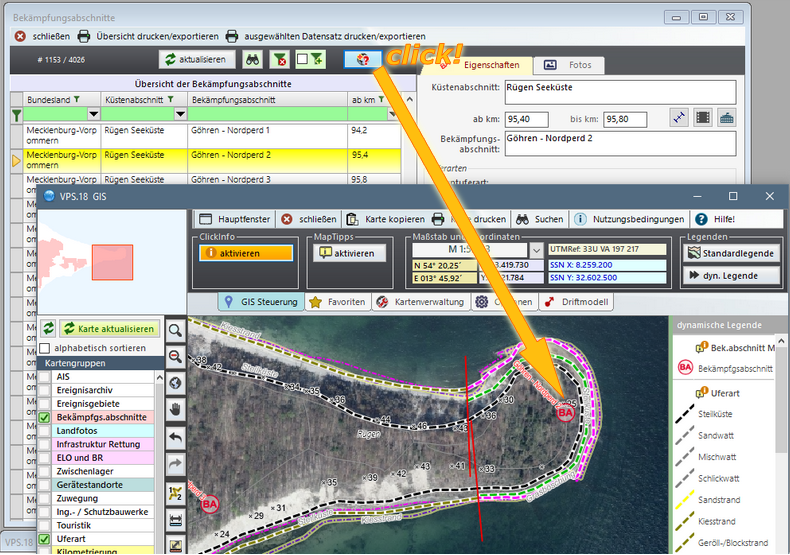
From the database it is possible, by using
the buttons of the user interface, to find
the answer to the question "Where is that?"
in a geo-referenced dataset (e.g. coastal
section, equipment store or response section).
This occurs by a programme-generated switch
to the GIS and a zoom to the object in
question.
|
 |
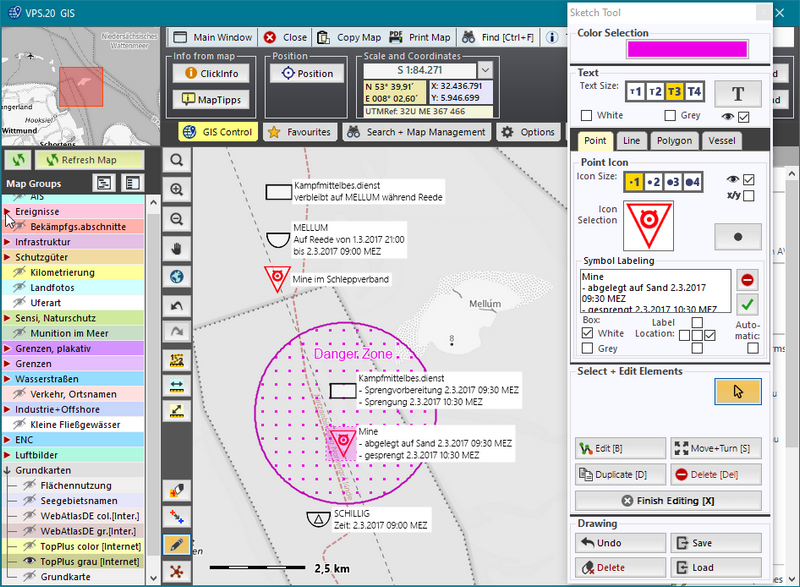
Apart from common map and layer organisation, functions adapted to
individual actions are available.
Different distances or area dimensions can be measured, and multi-coloured
drawings or texts for reports or response planning can be entered
via the map interface.
Together with the map, these elements can be printed as
true-to-scale maps or transferred into different graphics or text
programs. |
 |
Regarding the coordinate systems, the conflict between the often onshore-used cartesian coordinate systems and the coordinates used in marine data exchange had to be resolved. The solution was the permanet conversion of both coordinate systems by geomathematic functions in VPS. As a result, all geographic or cartesian data can be entered and they are available permanently in the coordinate display. To make VPS useable internationally VPS.system has
in use the
international useable UTM-coordinates as a cartesian coordinate
system.
Further fields of application for the GIS arise from an easy-to-use
drawing function, to track the current situation or to use the
implemented small drift model
developed by the German Federal Maritime Hydrographic Agency
(BSH) Hamburg. |
| |